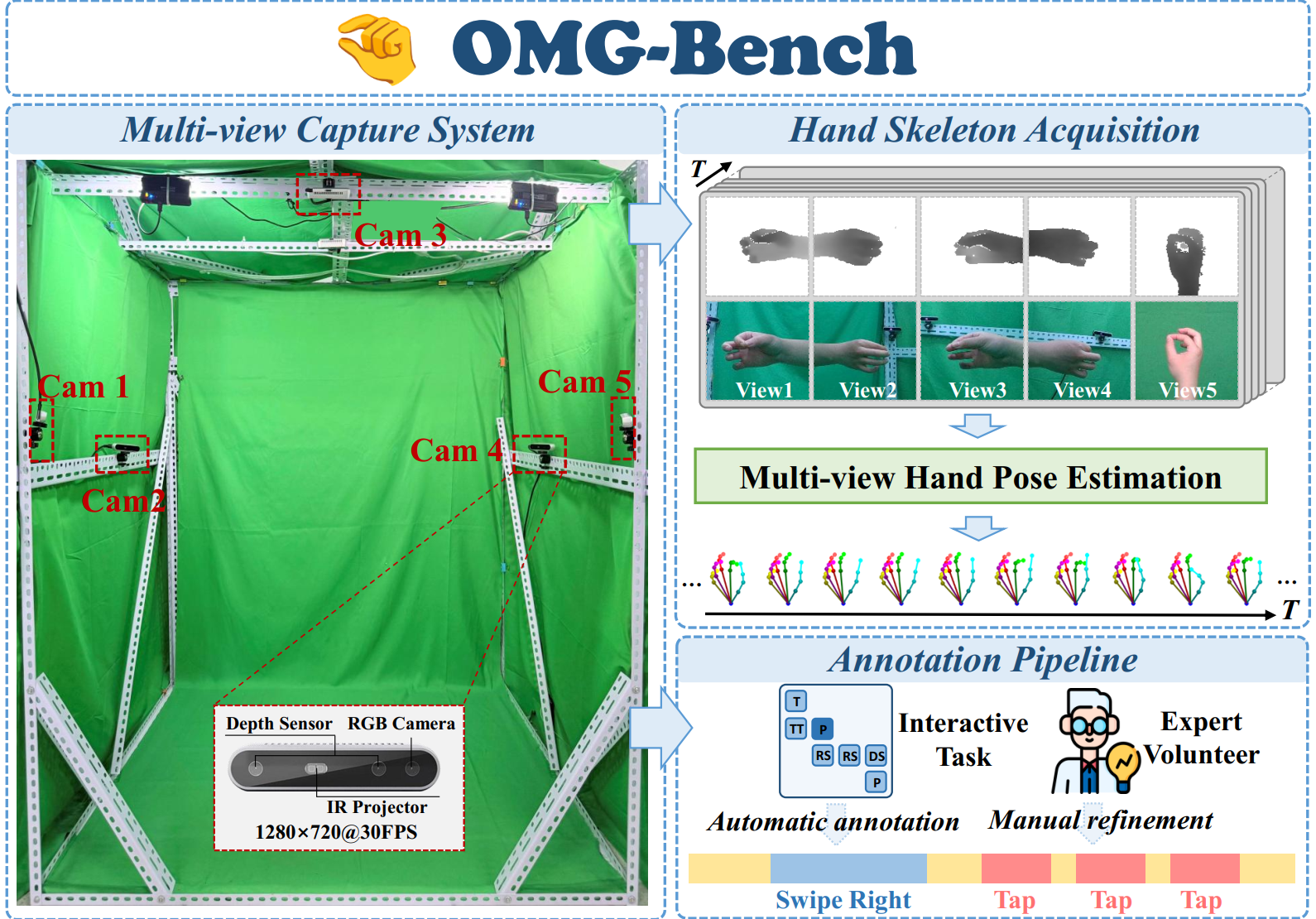
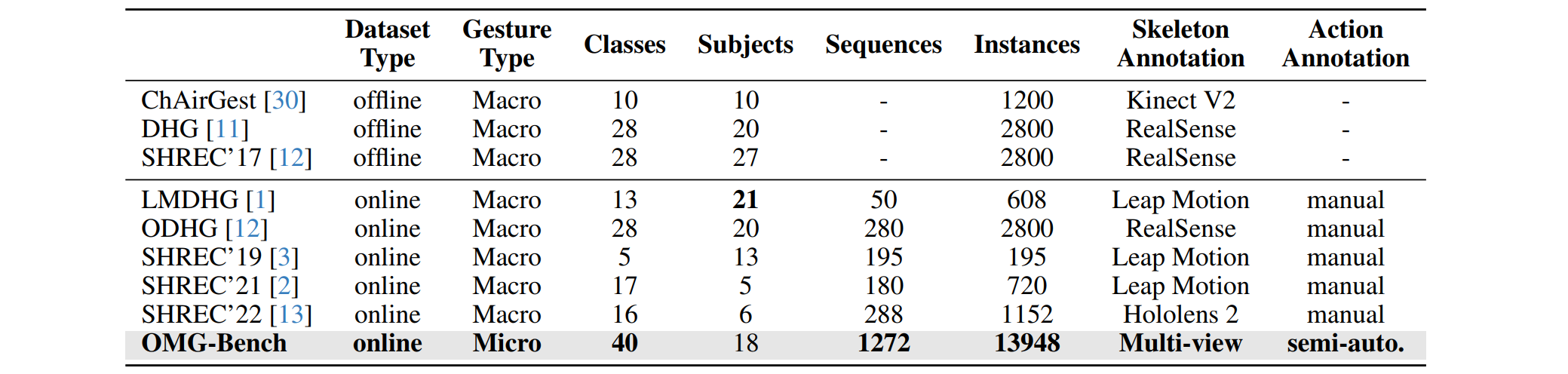
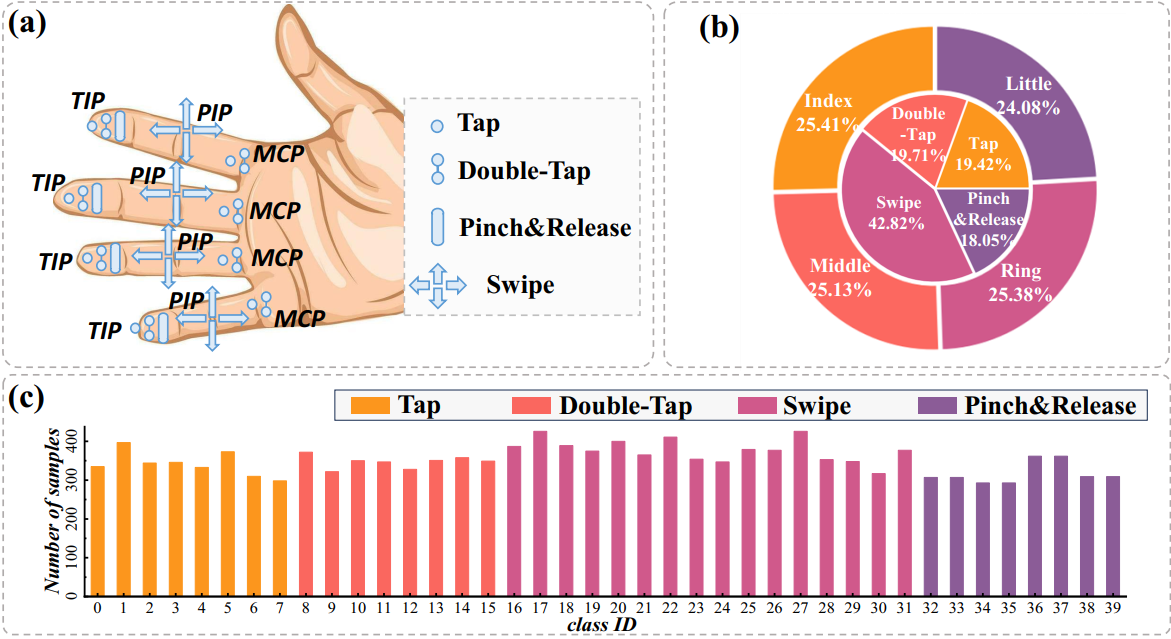
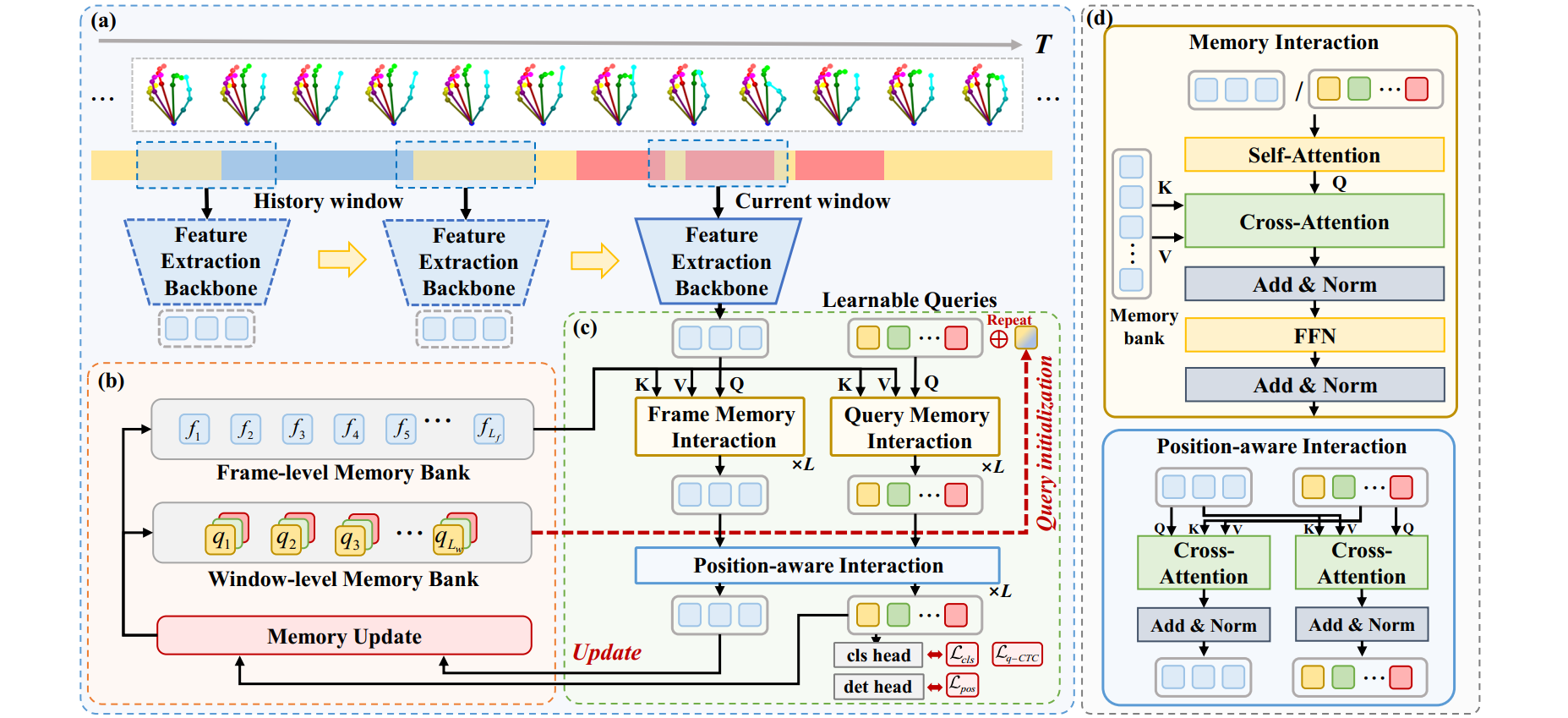
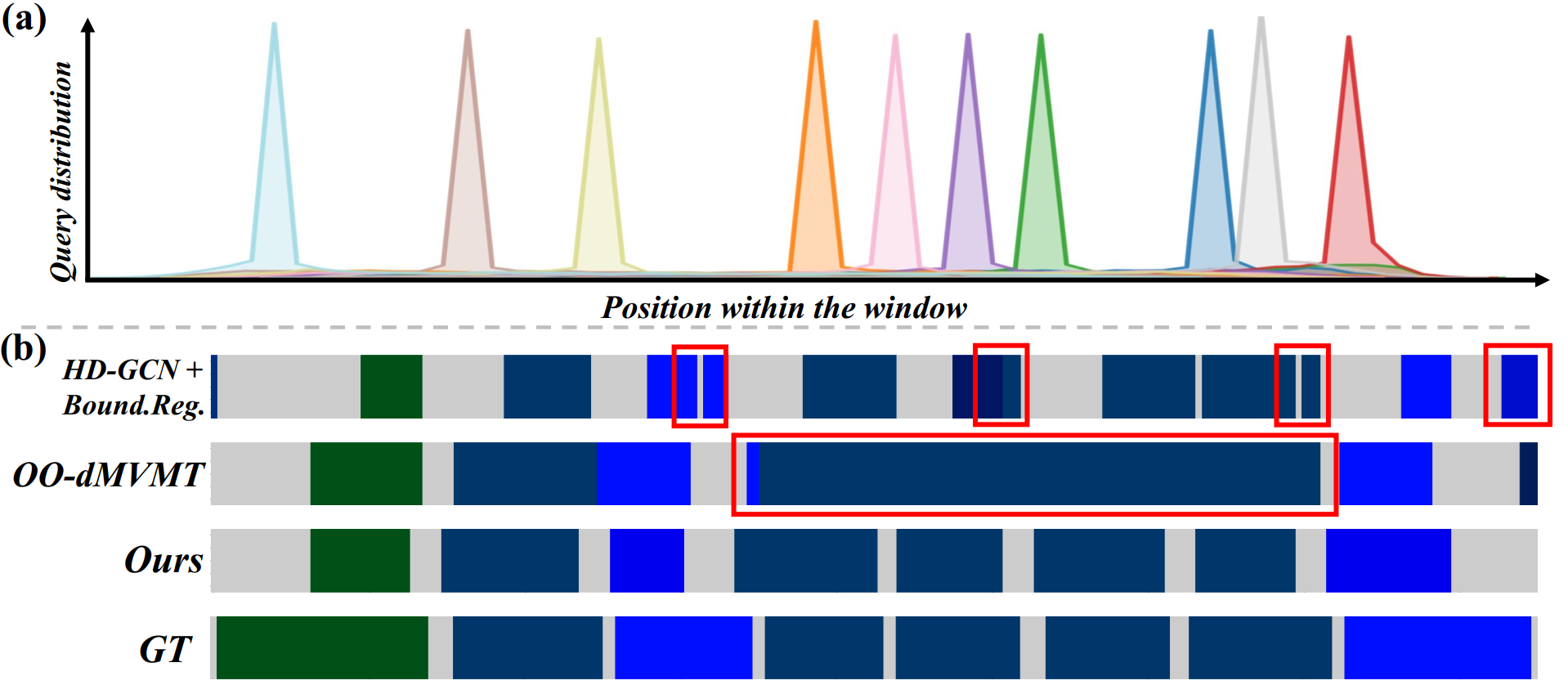
Online micro gesture recognition from hand skeletons is critical for VR/AR interaction but faces challenges due to limited public datasets and task-specific algorithms. Micro gestures involve subtle motion patterns, which make constructing datasets with precise skeletons and frame-level annotations difficult. To this end, we develop a multi-view self-supervised pipeline to automatically generate skeleton data, complemented by heuristic rules and expert refinement for semi-automatic annotation. Based on this pipeline, we introduce OMG-Bench, the first large-scale public benchmark for skeleton-based online micro gesture recognition. It features 40 fine-grained gesture classes with 13,948 instances across 1,272 sequences, characterized by subtle motions, rapid dynamics, and continuous execution. To tackle these challenges, we propose Hierarchical Memory-Augmented Transformer (HMATr), an end-to-end framework that unifies gesture detection and classification by leveraging hierarchical memory banks which store frame-level details and window-level semantics to preserve historical context. In addition, it employs learnable position-aware queries initialized from the memory to implicitly encode gesture positions and semantics. Experiments show that HMATr outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 7.6% in detection rate, establishing a strong baseline for online micro gesture recognition.